How Solar
Panels Work
If you’ve been looking for a way to save money on your electricity bills, solar panels can be an excellent addition to your home. Solar panels not only help reduce your energy costs but also benefit the environment.
Sunlight provides pure, renewable energy. It’s available to us whenever the sun shines, and it’s also among the cleanest energy sources on the planet.
Solar panels have been growing in popularity for some time. Many homeowners are seeing the benefits of solar power and choosing to invest in solar panels for their homes. More and more people are discovering that solar panels can help lower energy costs and reduce our impact on the environment, but not a lot of people know exactly how solar technology functions.
So, how do solar panels work? In this guide, we’ll be discussing the scientific process by which solar panels can take in energy from the sun and turn it into electricity that you can use in your home. We’ll tell you what solar panels are made of, how they work, and we’ll explain how much you can expect to spend on your own panels.
What are solar panels?
Solar panels transform light from the sun into usable energy through photovoltaic (PV) technology. Solar photovoltaic panels consist of a sheet of PV cells, a metal frame, a glass cover, and wiring.
One solar panel will contain many (usually 60-plus) PV cells configured in the shape of a square or rectangle. The more PV cells a panel has, the more energy it will be able to create. Solar panels are situated on a base structure that is bolted onto the roof of a home.
Every PV cell has two pieces of silicon (one on top of the other) that act as a semiconductor. To create an electrical field, the two pieces of silicon must have opposite electrical charges.
The silicone piece on top has been doped (infused) with phosphorus. The phosphorus adds electrons to the composition of the silicon piece, giving it a negative charge. The bottom piece of silicon has been doped with boron. The boron molecules decrease the amount of electrons in the silicon, giving the silicon a positive charge.
How solar cells work
Now that you know what PV panels are made of, you might be wondering how they can transform the sun’s rays into useful energy. The process by which solar panels produce electricity out of sunlight is called the photovoltaic effect. Here’s how it works.
Sunlight interacts with the solar panel and enters the PV cells. When light goes into a PV cell, photons (light energy particles) pass through the top, negatively charged silicon layer. When the photons reach the lower, positively charged silicon layer, their energy is transferred to electrons.
This causes the electrons in the lower layer to launch themselves into the upper layer. The electrons start to circulate and create an electric current. The upper silicone layer then sends the electrons through a circuit in the form of electricity.
How home solar panels work
Homeowners attach solar photovoltaic panels to their roofs to harness energy from the sun and fuel the appliances and systems in their homes. Typically, a solar panel installer gives the homeowner advice like which direction and what angle to position their panels for maximum energy production. In the United States, for example, solar panels should ideally face south.
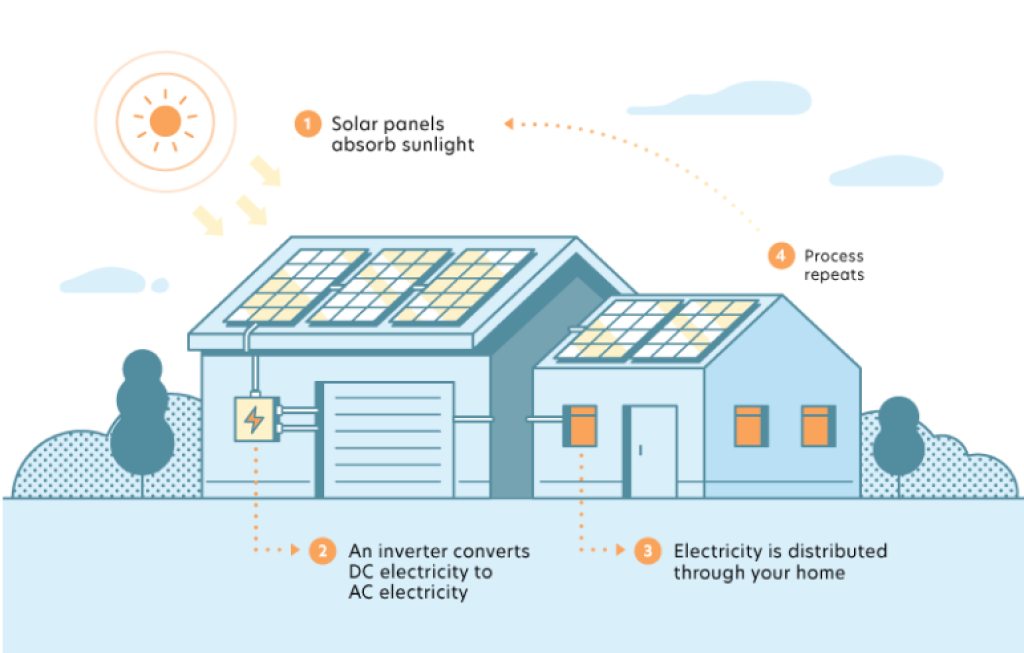
As we’ve already mentioned, each panel contains a sheet of photovoltaic cells to absorb sunlight and change it into electricity. But before the newly created electricity can be used in a home, it still needs to be changed from direct current (DC) electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity.
The device responsible for changing energy from DC electricity to AC electricity is called an inverter. Most solar energy systems won’t have more than one or two inverters, depending on the size of a home. Homeowners can also purchase microinverters that fasten to every panel in a system to increase the amount of electricity a system can produce.
After changing the electricity into AC electricity, the inverter sends the energy through a circuit to your breaker box. From there, the electricity is distributed to all your home appliances and systems.
While there are off-grid solar energy systems, most homes with solar panels still stay connected to their utility company’s electrical grid. The reason for this is that the amount of energy that solar panels can generate is dependent on the weather.
While solar panels still produce electricity on cloudy days, they won’t create nearly as much power as they could on a sunny day. There might be days when panels can’t create enough electricity to power a home efficiently. On those days, homeowners can still use power from their utility company.
There might be other times that a system produces more energy than a home needs. In these situations, the excess energy will flow back through the utility company’s power grid so that it can be distributed among consumers in the area. This process is called net metering. Generally, utility companies offer credits to solar energy users who share their extra energy.
How many solar panels does your home need?
The amount of solar panels that you need will depend on factors like how large your roof is and the volume of energy you want to produce. On average, a home solar energy system will have around 20 to 25 panels.
When you reach out to Vivint, we’ll connect you with a specialist who can survey your property and tell you exactly how many solar panels you need.
How much do solar panels cost?
There’s a lot of different variables that can affect the cost of home solar panels. The number of solar panels you’ll need, how much energy you want to create, the size and design of your panels, and any upgrades like microinverters can all affect the total price of your solar energy system.
While solar panels can save you money in the long run, they can require a substantial initial investment. Beyond the price of your panels themselves, you may also have to pay for things like state and local permits and installation.
Before you start planning out your solar energy system, you should have a ballpark of what your panels will cost you. A Vivint specialist will work with you to create a quote for a system that meets your energy needs. They’ll also share information about financing plans that can help make going solar more affordable.
How long do solar panels last?
On average, solar panels last around 25 to 30 years. However, you might need to replace other equipment in your system more often. For example, solar inverters usually only last around 10 to 15 years.
You may also have a battery for your solar panel system that allows you to store energy from the sun for later use. The life span of a solar battery will depend on how often you use it. If you only use a battery during an emergency, like a power outage, it can last well over 20 years. But if you use it as your main power source, it might stop working in as little as 10 years.
Discover how Vivint can help with your transition to a
smart home
Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to capture sunlight and transform it into electricity you can use to power your home. And unlike fossil fuels, solar energy doesn’t release any greenhouse gas emissions, like carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere.
A solar energy system can be a great addition to your home whether you’re environmentally conscious or just looking to save money on your utility bill over time. Solar panels can even increase the market value of your home and help you score government tax incentives, like the solar investment tax credit (ITC).
If you’re thinking about investing in solar panels or other smart home upgrades, request a consultation from a Vivint professional. Our experts can help you design your ideal smart home and security system, complete with smart products like lighting devices, sensors, locks, and cameras.