How Solar Inverters Work
Solar energy systems with photovoltaic (PV) panels have become a popular home upgrade among environmentally and budget-conscious consumers. The sun is an excellent source of clean, renewable energy that doesn’t release any greenhouse gasses, like carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. Better yet, solar panels can save homeowners a lot of money in energy costs over time.
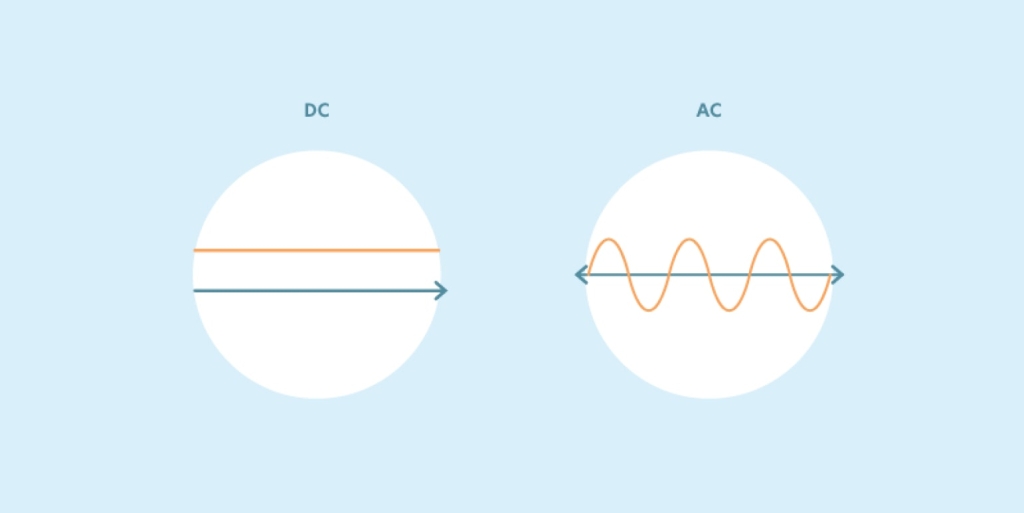
You might be surprised to learn that the sun’s energy doesn’t just fall to the earth in a form that we can use. Before we can use it, solar energy needs to be harnessed and altered from direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity.
That’s where an inverter comes in. An inverter is an essential part of any solar PV system. It converts DC electricity into AC electricity so that it can power a home or business. In this article, we’ll explain how an inverter system works and provide you with some key facts about inverters.
What is a solar inverter?
Inverters are power electronics (devices that manage the flow of electricity). The main function of the solar inverter is to convert DC electricity into AC electricity so the electrical grid can use the energy.
DC electricity keeps a steady voltage and can only flow in one direction. It is frequently used in low voltage applications like charging batteries. AC electricity can flow both ways, and its voltage can fluctuate from positive to negative. It is commonly used to power motors and can be found as the power source for refrigerators or dishwashers.
When it comes to powering solar panels, an inverter changes DC power to AC power by rapidly shifting the direction of the DC input forward and backward until the energy becomes an AC power output.
Although the main purpose of an inverter is to transform the sun’s energy into a usable state, modern inverters can have other duties as well. For example, an inverter might help your system maintain communication with computer networks.
Unlike normal inverters, a solar inverter system has a charge controller built in. Charge controllers regulate the amount of energy an inverter can take in. Charge controllers for solar inverters either have maximum power point tracking (MPPT) or pulse width modulation (PWM) functionality.
MPPT controllers let the inverter take in a greater amount of power and are pricier than PWM models. MPPT controllers also work better than PWM controllers on days when less direct sunlight reaches solar panels.
How a solar inverter works
Now that you understand the gist of what solar inverters do, you might be curious about how exactly they go about converting solar energy into energy you can use in your home. Here’s an in-depth explanation of how an inverter produces AC electricity out of DC electricity.

-
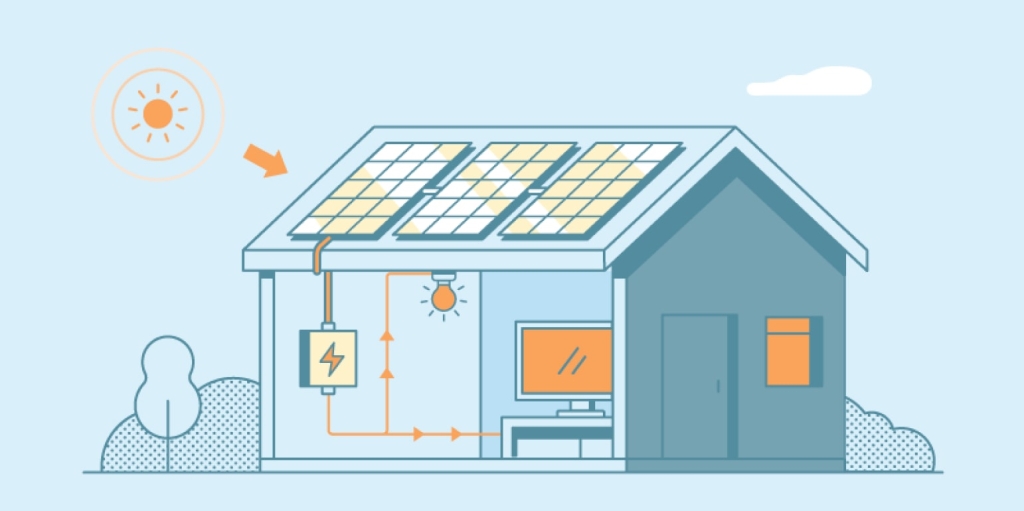
Direct current (DC) energy enters the inverter
After a PV panel creates electricity using the sun, the DC electricity needs to be transformed into AC electricity before it can be sent into a home. The PV cell sends the electricity down a cable toward the inverter to perform the change.
-
The inverter switches power current directions
Inside of an inverter, there are two pairs of transistors, or switches, arranged in a line of four. Transistor one operates in unison with transistor three, and transistor two operates in unison with transistor four. The transistors open and shut to reverse the flow of electricity.
-
The inverter outputs alternating current (AC) power
Whenever the DC electricity reaches a closed transistor, it's forced to change direction. The DC electricity is pushed back and forth over and over again until it eventually becomes AC electricity.
But why do the transistors need to work in pairs? As pairs of transistors take turns opening and shutting, the electric current gradually rises and falls. This makes a sine wave. Sine waves are shaped like rolling hills. It helps maintain a consistent current so electricity works reliably with your home appliances and systems.
If all the transistors opened and shut at the same time, the electricity would come out as a square wave. Electricity in square waves may not be safe to use in many of your devices.
How do inverters work with solar panels?
When the sun shines on solar cells on a panel, photons knock electrons loose from a semiconductor wafer. The wafer is usually made from silicon. The separated electrons form an electric current.
However, the current is DC electricity, and DC energy doesn’t work in home or business appliances. A solar power system needs inverters to transform the energy it generates into AC electricity.
Inverters can also serve as safety mechanisms for solar panel systems. When an inverter is tied to a utility company’s power grid (also known as grid-tied), it has an isolation switch that cuts the inverter off from the greater electricity grid if its power falls below acceptable levels.
The isolation switch stops the system from shooting electricity through power lines when crews are performing maintenance on them. Unfortunately, the isolation function will also stop your inverter from delivering electricity to your home during a blackout.
If you still want your panels to work during a blackout, you’ll have to use a solar battery backup system. A solar battery will store the energy that your system generates during the day. Energy systems that use solar batteries have specially designed inverters that allow them to still deliver electricity to the battery during power outages.
Off-grid systems (energy systems that work independently of a utility grid) also need solar batteries and specialized off-grid inverters to function. However, most homes use a grid tie inverter (an inverter that allows a solar energy system to connect to a power grid), so they can use power from the utility company on days when there might not be ample sunlight.
How many inverters does each solar panel need?
The number of inverters you’ll need for your system will depend on the type of inverter you use. There are a few main types of solar inverters that you can choose from.
- Single-phase inverters (also known as string inverters) are standalone boxes installed near the main service panel and electricity meter. A solar array (arrangement of panels) will likely only need one or two single-phase inverters depending on the size of the roof. Some single inverters also have power optimizers that prime DC electricity before it enters the inverter. This allows the inverter to work more efficiently.
- Microinverters do the same thing as single-phase inverters, but they’re much smaller. They’re roughly the size of an internet router. A solar system will generally have several microinverters, one attached to each individual panel.
- Central inverters are large inverters generally used for large commercial properties and businesses rather than homes. One central inverter can work with a huge number of solar panels.
- Battery inverters and hybrid inverters allow your solar panels to work with a battery. A battery inverter is a great option for an off-grid system. It sends energy directly to your switchboard instead of the power grid. A hybrid inverter (or a multi-mode inverter) has a DC charger that allows a battery to refuel using DC electricity.
How much do solar inverters cost?
There are a lot of factors that affect the price of an inverter, as well as the price of an entire solar energy system. The type of inverter (or inverters) you use, the amount of energy you want your system to generate, and the size of your home can all play a part in determining how much your inverter will cost.
When you reach out to Vivint, we’ll put you in touch with a solar installation specialist who can answer your questions about solar energy systems and give you a free quote for a system that will meet your energy needs. Your specialist can also educate you about financing plans that can help make your system more affordable.
How long do solar inverters last?
Inverters have electrical components that can wear out over time. While solar panels typically have a life span of around 25 to 30 years, solar inverters have a shorter, yet still lengthy, life span of around 10 to 15 years. You’ll likely have to replace your inverter at some point during the life of your solar panels to get optimal energy production from your system.
Make your transition to a smart home easy with help from Vivint
Without an inverter, you won’t be able to use the electricity that your solar panels create. Inverters alter the energy your panels capture so that it can power your home. Solar inverters are crucial components in the process of collecting and using solar energy.
If you’re interested in installing solar panels on your roof or making other smart home upgrades, take a look at some of the quality products Vivint has to offer. We have cutting-edge smart products like thermostats, lighting supplies, and security systems that make it easy to manage your home, even when you’re not there.
Take advantage of a free consultation with one of our experts. Not only will they answer any questions you might have, but they’ll also walk you through the process of designing and installing your ideal smart home setup.